煤及页岩气团队在深部煤储层孔隙表征及甲烷吸附量计算方面取得新进展
近日,太阳官网煤及页岩气团队的魏强,冯松宝,姜玮等教师在美国化学协会(American Chemical Society,ACS)下的Energy Fuels杂志发表了题为“Methane Adsorption Capacity of Deep-Buried Coals Based on PoreStructure in the Panji Deep Area of Huainan Coalfield, China(DOI:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c03800)”的文章,该期刊为JCR2区,为能源、燃料、化学与化工领域的国际著名权威期刊,2019年影响因子为3.421。
论文摘要如下:
Pore structure characterization of deep-buried coals and its implications on methane adsorption capacity are of great significance for further understanding adsorption mechanism of methane molecules by pores in deep strata. In this study, a series of several experiments, including high-pressure mercury intrusion porosimetry (HMIP), N2/CO2 adsorption, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and methane adsorption, were used to investigate the pore structure and methane adsorption capacity of deep-buried coals from the Panji Deep Area in Huainan Coalfield, China. The methane adsorption capacity of coal samples was obtained by experiment and correction based on the results by tests, and molecular simulation, the latter one adopted the pore filling and monolayer coverage theories. Results show that deep-buried coals developed with multiple types of pores and microfractures. Micropores provide the majority of specific surface area, whereas the pore volume of deep-buried coals is dominated by macropores. On the basis of experiments, the measured methane adsorption capacity of deep coals shows a medium to high value compared with the adjacent coalmines. the corrected methane adsorption capacity is in the range of 14.56−24.07 cm3/g with average of 18.91 cm3/g. The number of methane molecules adsorbed as a state of micropore filling is 32.98−59.83 × 1019 pcs, whereas of which in a form of monolayer coverage is 0.51−2.05 × 1019 pcs, the former is the primary contributor and accounts for 94.98−98.46% of the total. Notably, molecular simulated volume is close to that of measured methane adsorption volume, and both of them are significantly and positively correlated with volume and specific surface area of micropores. Methane adsorption capacity is depended on the micropore volume and external surface area, and the adsorption process is consisted by majority of micropore filling and a small amount of monolayer coverage.
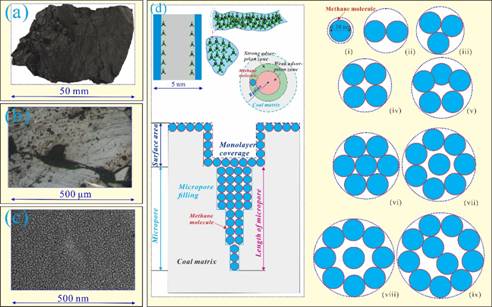
Figure 14. Methane adsorption mechanism in micropores.