近日,太阳官网水文与水资源工程教研室付敦老师以第一作者在Journal of Environmental Management (中科院二区Top期刊;影响因子:5.647)上发表题为“Arsenic removal in aqueous solutions using FeS2 (/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112246)”的研究论文,该研究工作得到了古天乐太阳娱乐集团tyc493博士科研启动项目(2019jb14)的资助与国家煤矿水害防治工程技术研究中心的平台支持。
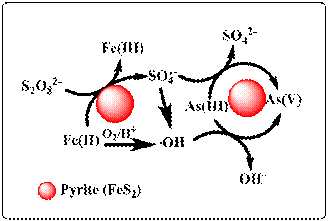
摘要:This study tested the technical feasibility of pyrite and persulfate oxidationsystem for arsenic (As) removal from aqueous solutions. The effects of persulfate on As removal by the pyrite in the integrated treatment were investigated. Prior to the persulfate addition into the reaction system, the physico-chemical interactions between As and the pyrite alone in aqueous solutions were explored in batch studies. The adsorption kinetics and isotherms of As removal by the pyrite were studied, while its removal mechanisms by the adsorbent were presented. At the same As concentration of 7.5 mg/L, it was found that As(III) attained a longer equilibrium time (8 h) than As(V) (2 h), while the pyrite had the ability to work effectively at pH ranging from 6 to 11. At optimum conditions (0.25 g/L of pyrite, pH 6.0 and 7.5 mg/L of As(III) concentration), the addition of persulfate(0.5 mM) into the reaction promoted acomplete removal of arsenic from the solutions.Consequently, this enabled the treated effluents to meet the maximum contaminant limit (MCL) of As according to the national legislation and the World Health Organization (WHO)’s requirement of <10 μg/L. Overall, this finding reveals the applicability of the pyrite as a natural material for water treatment and uncovers the importance of persulfate addition to promote a complete As removal from aqueous solutions.